Mybatis-Plus增删查改操作
增加
增加操作由于Mybatis-plus已经封装好了,所以直接可以调用service层的save函数,或者mapper层的insert函数
service层
//service层包装了几个方法
boolean save(T entity);//保存一个
boolean saveOrUpdate(T entity);//更新或者插入,有主键存在就执行更新,如果没有主键就执行插入,批量
@Transactional(
rollbackFor = {Exception.class}
)
default boolean saveBatch(Collection<T> entityList) { //保存多个,传入List,默认的batchSize为1000
return this.saveBatch(entityList, 1000);
}
boolean saveBatch(Collection<T> entityList, int batchSize);//存多个,传入List,可以指定batchSize大小
@Transactional(
rollbackFor = {Exception.class}
)
default boolean saveOrUpdateBatch(Collection<T> entityList) {//批量更新或者插入,有主键存在就执行更新,如果没有主键就执行插入
return this.saveOrUpdateBatch(entityList, 1000);
}
boolean saveOrUpdateBatch(Collection<T> entityList, int batchSize);//同上,可以指定batchsize大小
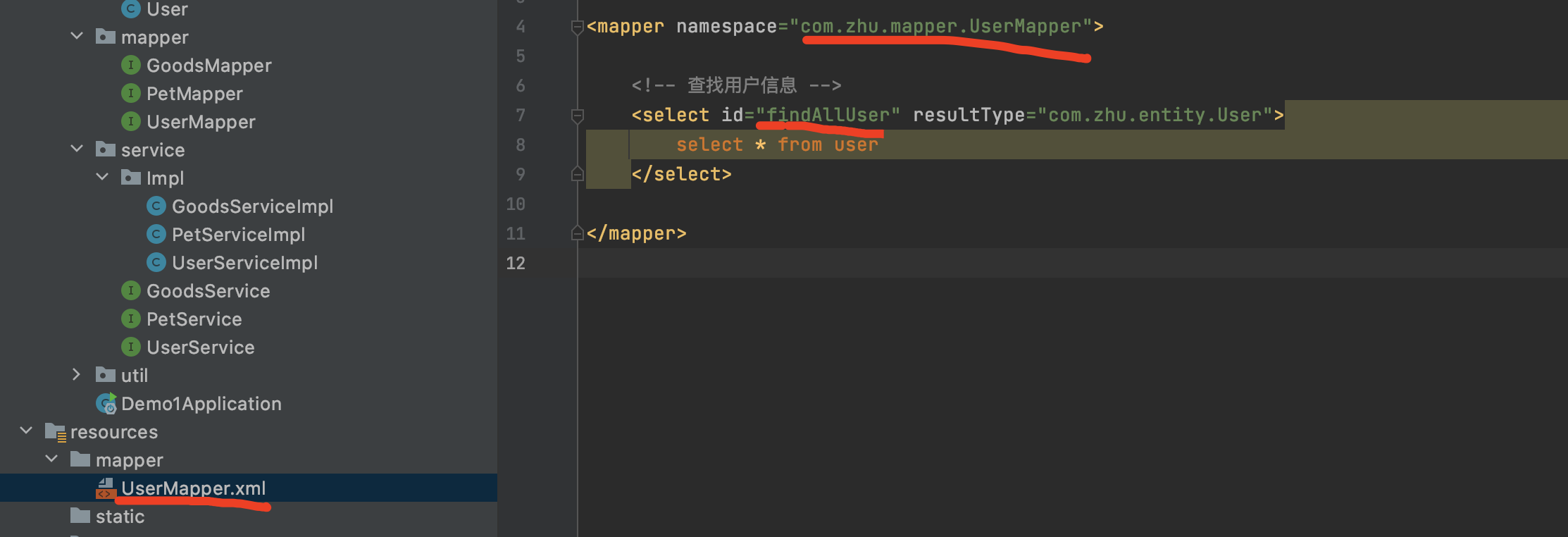
mapper层
int insert(T entity);//使用时插入对象
userMapper.insert(user);使用
void save() {
User user = new User();
user.setName("test");
user.setPaswword("123");
// 1.使用service新增
userService.save(user);
// 2.使用mapper 新增
userMapper.insert(user);
}删除
service层
//service层中包含了4个方法
boolean removeById(Serializable id);//通过id来删除
boolean removeByMap(Map<String, Object> columnMap);//Map里存放条件
boolean remove(Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);//使用Wrapper语句
boolean removeByIds(Collection<? extends Serializable> idList);//通过id批量删除mapper层
可以发现,与service层其实是一一对应的,不用看源码就可以知道,mybatis-plus的封装service层用了mapper的函数。
int deleteById(Serializable id);//通过id删除
int deleteByMap(@Param("cm") Map<String, Object> columnMap);//通过mapper属性来删除,mapper可以放多个条件属性
int delete(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> wrapper);//通过wrapper语句来删除
int deleteBatchIds(@Param("coll") Collection<? extends Serializable> idList);//通过批量id来批量删除使用
//根据 id 删除
@Test
public void testDelete(){
userMapper.deleteById(1278951504018575369L);
}
//根据 id 批量删除
@Test
public void testDeleteBatchIds(){
userMapper.deleteBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1278951504018575367L,1278951504018575368L));
}
//使用 map 删除
@Test
public void testDeleteByMap(){
HashMap<String, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("age",200);
userMapper.deleteByMap(hashMap);
}
//使用wapper语句
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper
.isNull("name")
.ge("age", 12)
.isNotNull("email");
int result = userMapper.delete(queryWrapper);//返回删除的数量Mybatis中的逻辑删除
物理删除:从数据库中直接删除数据
逻辑删除:并没有在数据库中直接删除数据,而是通过一个变量,让这个数据失效
逻辑删除目的:防止数据的丢失,管理员可以看见删除的数
首先修改数据库,增加 deleted 字段,默认为 0
修改实体类,并添加注释
@TableLogic private Integer deleted;配置 properties
mybatis-plus.global-config.db-config.logic-not-delete-value=0 mybatis-plus.global-config.db-config.logic-delete-value=1测试
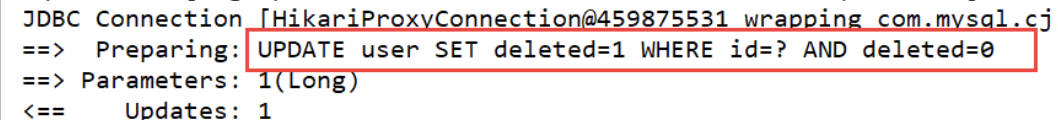
//逻辑删除 @Test public void testLogicDelete(){ userMapper.deleteById(1L); }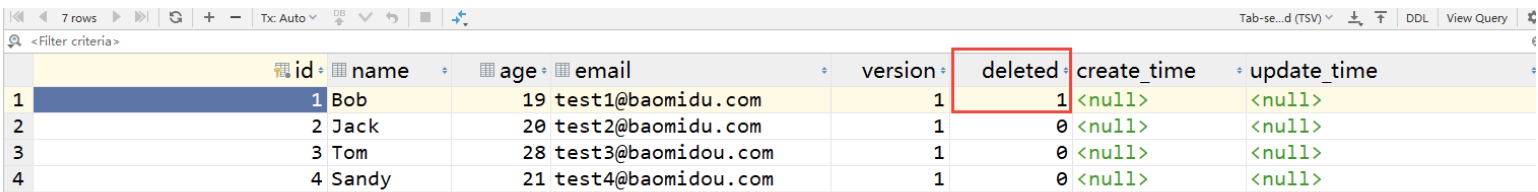
可以看到走的是更新操作:
同样,我们假如对逻辑表的查询和更新操作,会自动帮我们加上deleted=0的属性值,
如查询:
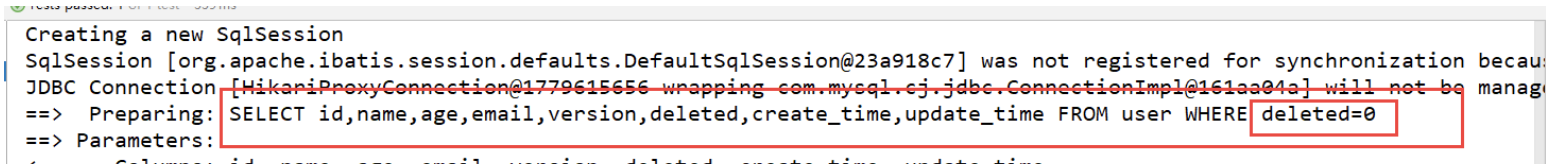
deleted=1的已经删除的记录,查询不出
更新
service层
boolean updateById(T entity);//通过id来更新,传入的是实体,实体中包含了id,entity有什么属性就更新什么属性
boolean update(T entity, Wrapper<T> updateWrapper);//entity为需要更新的值,wrapper语句为条件条件,entity有什么属性就更新什么属性
default boolean update(Wrapper<T> updateWrapper) { //默认第一个传入null,需要更新的属性的值,可以在wrapper语句中设置
return this.update((Object)null, updateWrapper);
}
@Transactional(
rollbackFor = {Exception.class}
)
default boolean updateBatchById(Collection<T> entityList) { //批量更新,传入一个List,默认的batchSize为1000
return this.updateBatchById(entityList, 1000);
}
boolean updateBatchById(Collection<T> entityList, int batchSize);//批量更新,可以指定batchSize大小
boolean saveOrUpdate(T entity);//批量更新或者插入,有主键存在就执行更新,如果没有主键就执行插入mapper层
int updateById(@Param("et") T entity);//传入entity,entity自带id 属性,entity有什么属性就更新什么属性
int update(@Param("et") T entity, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> updateWrapper);//传入entity为更新的值,wrapper为条件语句,entity有什么属性就更新什么属性使用
@Test
void update() {
User user = new User();
user.setAge(23);
user.setEmail("344");
user.setName("test333");
UpdateWrapper<User> updateWrapper = new UpdateWrapper<>();
updateWrapper.eq("id","1");
// 1.user 中封装修改的属性值, updateWrapper 中封装修改的条件参数值
userService.update(user,updateWrapper);
// 2.根据条件修改对应的参数属性值,下语句对应,set name 2 where age= 23
userService.update(Wrappers.<User>update().lambda().set(User::getName, "2").eq(User::getAge, 23));
// 3.判断参数是否为空,并进行修改
String name = "name";
userService.update(Wrappers.<User>update().lambda().set(StringUtils.isNotBlank(name),User::getName, name).eq(User::getAge, 23));
// 4.不实用lamda表达式
//修改值
User user = new User();
user.setAge(99);
user.setName("Andy");
//修改条件
UpdateWrapper<User> userUpdateWrapper = new UpdateWrapper<>();
userUpdateWrapper.like("name", "h")
.or()
.between("age", 20, 30);
/*相当于
UPDATE user
SET name=?, age=?, update_time=?
WHERE deleted=0 AND name LIKE ? OR age BETWEEN ? AND ?
*/
int result = userMapper.update(user, userUpdateWrapper);
// 5.
//修改值
User user = new User();
user.setAge(99);
//修改条件
UpdateWrapper<User> userUpdateWrapper = new UpdateWrapper<>();
userUpdateWrapper.like("name", "h")
.set("name", "老李头")//除了可以查询还可以使用set设置修改的字段
.setSql(" email = '123@qq.com'");//可以有子查询
/*
UPDATE user
SET age=? name=?, email = ‘123@qq.com’
WHERE deleted=0 AND name LIKE ?
*/
int result = userMapper.update(user, userUpdateWrapper);
}查询
service层
T getById(Serializable id);//通过id查询
Collection<T> listByIds(Collection<? extends Serializable> idList);//通过多个id查询多个id
Collection<T> listByMap(Map<String, Object> columnMap);//通过map属性键对值查询
default T getOne(Wrapper<T> queryWrapper) { //通过wrapper语句查询一条记录,默认抛出异常,
return this.getOne(queryWrapper, true);
}
T getOne(Wrapper<T> queryWrapper, boolean throwEx);//通过wrapper语句查询一条记录,可以指定throwEx
Map<String, Object> getMap(Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);//通过wrapper语句,查询一条记录,返回的形式是map
int count(Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);//查询符合条件的数量
default int count() {
return this.count(Wrappers.emptyWrapper());//默认是0条
}
List<T> list(Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);//通过wrapper语句查询,返回对象的list
default List<T> list() { //默认空查询,即返回空
return this.list(Wrappers.emptyWrapper());
}
IPage<T> page(IPage<T> page, Wrapper<T> queryWrapper); // 翻页查询
default IPage<T> page(IPage<T> page) { // 翻页查询,默认空查询
return this.page(page, Wrappers.emptyWrapper());
}
List<Map<String, Object>> listMaps(Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);// 查询列表,返回map 的List
default List<Map<String, Object>> listMaps() {
return this.listMaps(Wrappers.emptyWrapper());
}mapper层
T selectById(Serializable id);//通过id查询
List<T> selectBatchIds(@Param("coll") Collection<? extends Serializable> idList);//通过多个id的List查询多条记录
List<T> selectByMap(@Param("cm") Map<String, Object> columnMap);//通过Map键值对来查询记录
T selectOne(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);//查询一条记录
Integer selectCount(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);//条件符合的记录数量
List<T> selectList(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);//通过Wrapper来查询记录
List<Map<String, Object>> selectMaps(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);//通过Wrapper来查询记录,返回的是Map属性对的List
List<Object> selectObjs(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);//通过Wrapper查询,返回Object的List
IPage<T> selectPage(IPage<T> page, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);//分页查询
IPage<Map<String, Object>> selectMapsPage(IPage<T> page, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);//分页查询分页查询
在配置类中增加配置
//分页插件 @Bean public PaginationInterceptor paginationInterceptor() { return new PaginationInterceptor(); }Page 中的参数有两个:long current、long size。current 表示了当前页数,size 表示了每页数据个数
//分页插件 @Test public void testPage(){ //selectPage(IPage<T> var1,Page 是 Ipage的实现类 // Page的参数有两个,long current, long size // 第一个是当前页, // 第二个是每页显示数据的个数 Page<User> userPage = new Page<>(1,5); userMapper.selectPage(userPage,null); userPage.getRecords().forEach(System.out::println); System.out.println(userPage.getTotal()); //数据的总数 System.out.println(userPage.getCurrent()); //当前页数 }实际上,MyBatisPlus 的分页底层采用的还是 limit
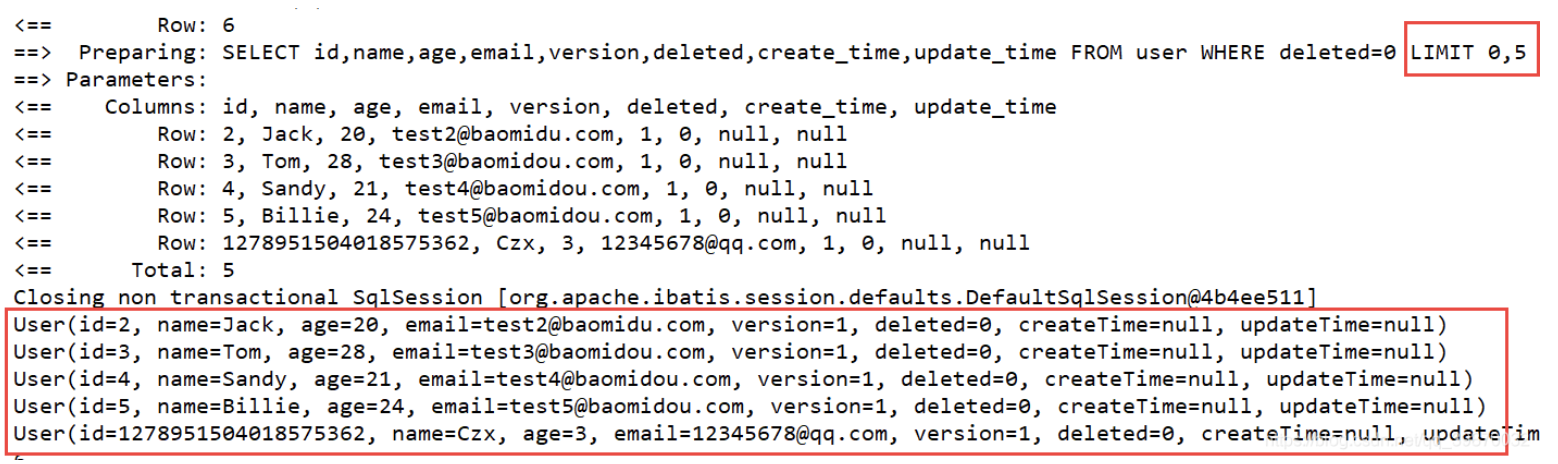
使用
//下面是许多查询操作
@Test
//通过id查询
public void testSelectById(){
User user = userMapper.selectById(1L);
}
//批量查询用户
@Test
public void testSelectBatchIds(){
List<User> users = userMapper.selectBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3));
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
//按条件查询,使用 map 查询
@Test
public void testSelectByMap(){
HashMap<String, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
//map 里放的是查询的条件 查询名字是 Czx 的人的信息
hashMap.put("name","Czx");
//条件可以拼接,往进 put 一个,就是一个条件 WHERE name = ? AND age =
hashMap.put("age",200L);
List<User> users = userMapper.selectByMap(hashMap);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
//
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.notLike("name", "e")
.likeRight("email", "t");
//返回值是Map列表
List<Map<String, Object>> maps =
userMapper.selectMaps(queryWrapper);
maps.forEach(System.out::println);
Wrapper构造器
Wrapper类的结构
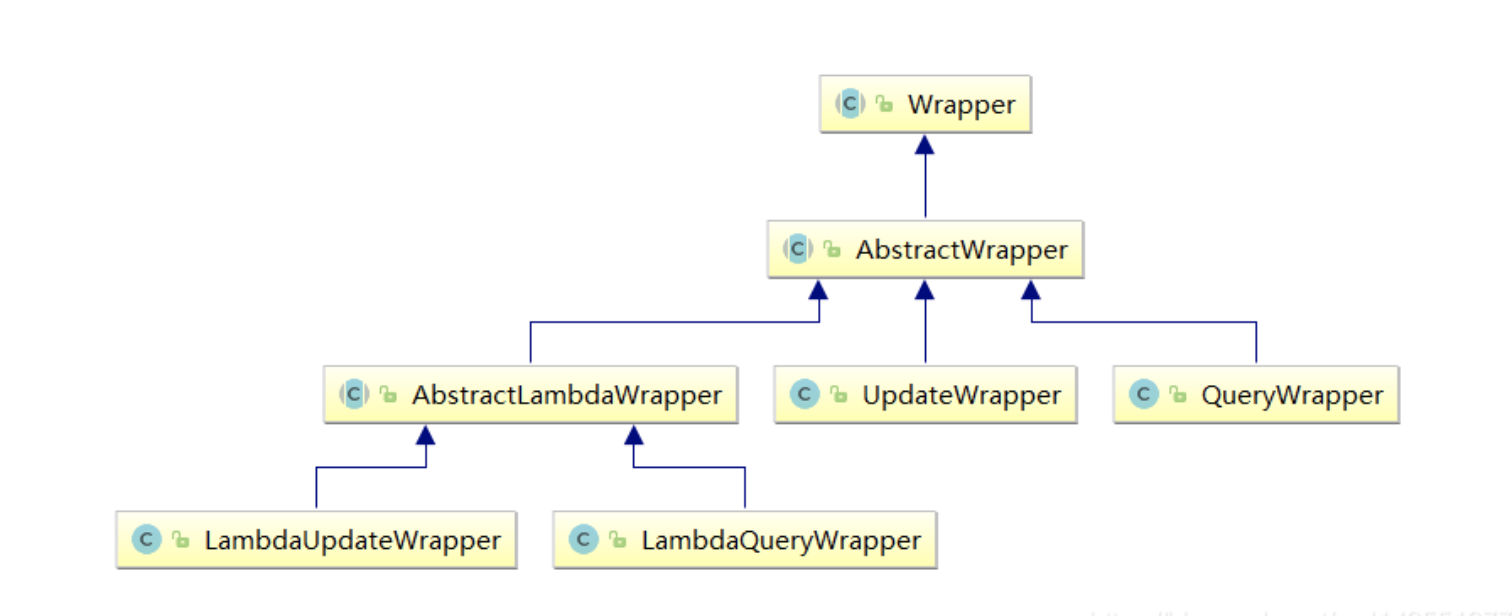
- AbstractWrapper: 用于查询条件封装,生成sql的where条件
- AbstractLambdaWrapper: Lambda语法使用Wrapper统一处理解析lambda获取column
- QueryWrapper: Entity 对象封装操作类,不是用lambda
- UpdateWrapper: Update条件封装,用于Entity对象更新操作
常用的为QueryWrapper&UpdateWrapper
常见用法
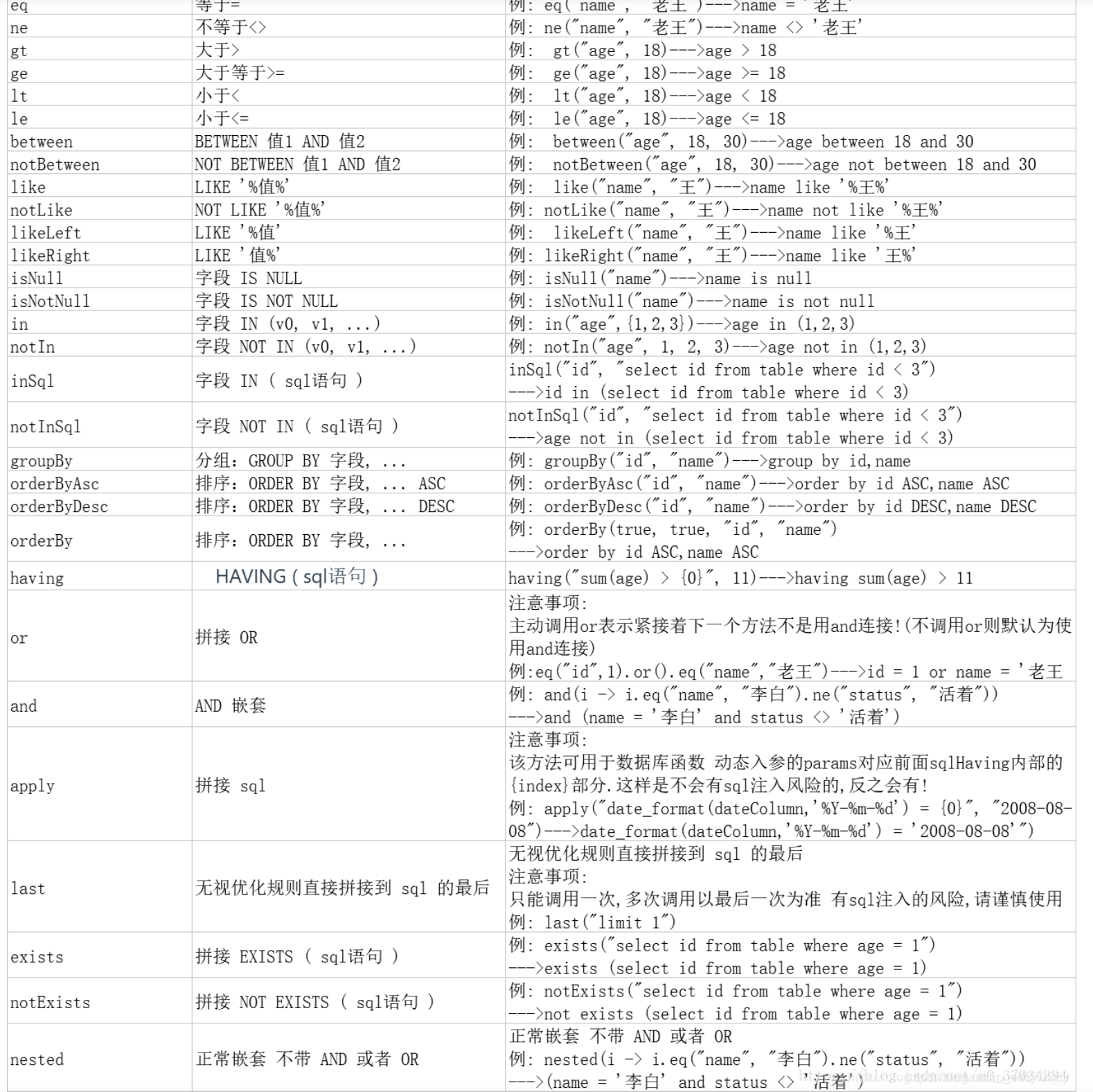
- allEq:全部eq(或个别isNull)
例1: allEq({id:1,name:"老王",age:null})--->id = 1 and name = '老王' and age is null 例2: allEq({id:1,name:"老王",age:null}, false)--->id = 1 and name = '老王' - eq:等于 =
例1: allEq((k,v) -> k.indexOf("a") > 0, {id:1,name:"老王",age:null})--->name = '老王' and age is null 例2: allEq((k,v) -> k.indexOf("a") > 0, {id:1,name:"老王",age:null}, false)--->name = '老王' - ne:不等于 <>
例: ne("name", "老王")--->name <> '老王' - gt:大于 >
例: gt("age", 18)--->age > 18 - ge:大于等于 >=
例: ge("age", 18)--->age >= 18 - lt:小于 <
例: lt("age", 18)--->age < 18 - le:小于等于 <=
例: le("age", 18)--->age <= 18 - between:BETWEEN 值1 AND 值2
例: between("age", 18, 30)--->age between 18 and 30 - notBetween:NOT BETWEEN 值1 AND 值2
例: notBetween("age", 18, 30)--->age not between 18 and 30 - like:LIKE ‘%值%’
例: like("name", "王")--->name like '%王%' - notLike:NOT LIKE ‘%值%’
例: notLike("name", "王")--->name not like '%王%' - likeLeft:LIKE ‘%值’
例: likeLeft("name", "王")--->name like '%王' - likeRight:LIKE ‘值%’
例: likeRight("name", "王")--->name like '王%' - isNull:字段 IS NULL
例: isNull("name")--->name is null - isNotNull:字段 IS NULL
例: isNotNull("name")--->name is not null - in:字段 IN (value.get(0), value.get(1), …)
例: in("age",{1,2,3})--->age in (1,2,3) - notIn:字段 IN (value.get(0), value.get(1), …)
例: notIn("age",{1,2,3})--->age not in (1,2,3) - inSql:字段 IN ( sql语句 )
例: inSql("age", "1,2,3,4,5,6")--->age in (1,2,3,4,5,6) 例: inSql("id", "select id from table where id < 3")--->id in (select id from table where id < 3) - notInSql:字段 NOT IN ( sql语句 )
例: notInSql("age", "1,2,3,4,5,6")--->age not in (1,2,3,4,5,6) 例: notInSql("id", "select id from table where id < 3")--->age not in (select id from table where id < 3) - groupBy:分组:GROUP BY 字段, …
例: groupBy("id", "name")--->group by id,name - orderByAsc:排序:ORDER BY 字段, … ASC
例: orderByAsc("id", "name")--->order by id ASC,name ASC - orderByDesc:排序:ORDER BY 字段, … DESC
例: orderByDesc("id", "name")--->order by id DESC,name DESC - orderBy:排序:ORDER BY 字段, …
例: orderBy(true, true, "id", "name")--->order by id ASC,name ASC - having:HAVING ( sql语句 )
例: having("sum(age) > 10")--->having sum(age) > 10 例: having("sum(age) > {0}", 11)--->having sum(age) > 11 - or:拼接 OR 。注意事项:主动调用or表示紧接着下一个方法不是用and连接!(不调用or则默认为使用and连接)
例: eq("id",1).or().eq("name","老王")--->id = 1 or name = '老王' 例: or(i -> i.eq("name", "李白").ne("status", "活着"))--->or (name = '李白' and status <> '活着') - and:AND 嵌套
apply:拼接 sql 。 注意事项:该方法可用于数据库函数 动态入参的params对应前面sqlHaving内部的{index}部分.这样是不会有sql注入风险的,反之会有!例: and(i -> i.eq("name", "李白").ne("status", "活着"))--->and (name = '李白' and status <> '活着')例: apply("id = 1")--->having sum(age) > 10 例: apply("date_format(dateColumn,'%Y-%m-%d') = '2008-08-08'")--->date_format(dateColumn,'%Y-%m-%d') = '2008-08-08'") 例: apply("date_format(dateColumn,'%Y-%m-%d') = {0}", "2008-08-08")--->date_format(dateColumn,'%Y-%m-%d') = '2008-08-08'") - last:无视优化规则直接拼接到 sql 的最后。注意事项:只能调用一次,多次调用以最后一次为准 有sql注入的风险,请谨慎使用
例: last("limit 1") - exists:拼接 EXISTS ( sql语句 )
例: exists("select id from table where age = 1")--->exists (select id from table where age = 1) - notExists:拼接 NOT EXISTS ( sql语句 )
例: notExists("select id from table where age = 1")--->not exists (select id from table where age = 1) - nested:正常嵌套 不带 AND 或者 OR
例: nested(i -> i.eq("name", "李白").ne("status", "活着"))--->(name = '李白' and status <> '活着')
构建复杂的数据库操作
先构造Wrapper语句,可以直接在service层上构造wrapper语句。
在service层上封装函数,构造wrapper语句 使用mapper的方法,在service层上封装成一个函数,这样controller可以直接传参调用service层的函数。
mapper接口文件中定义好方法,然后在对应的xml文件中,编写对应的SQL就好,最后还是要在service层上将mapper的函数进行封装。